Highlights
- • Incomplete recovery for AOF results from washing step and incomplete combustion
- • Incomplete recovery for EOF results from washing step and incomplete elution
- • The washing step for AOF and EOF is essential and effective for fluoride removal
- • EOF outperformed AOF in terms of average recoveries for the 10 selected PFAAs
Abstract
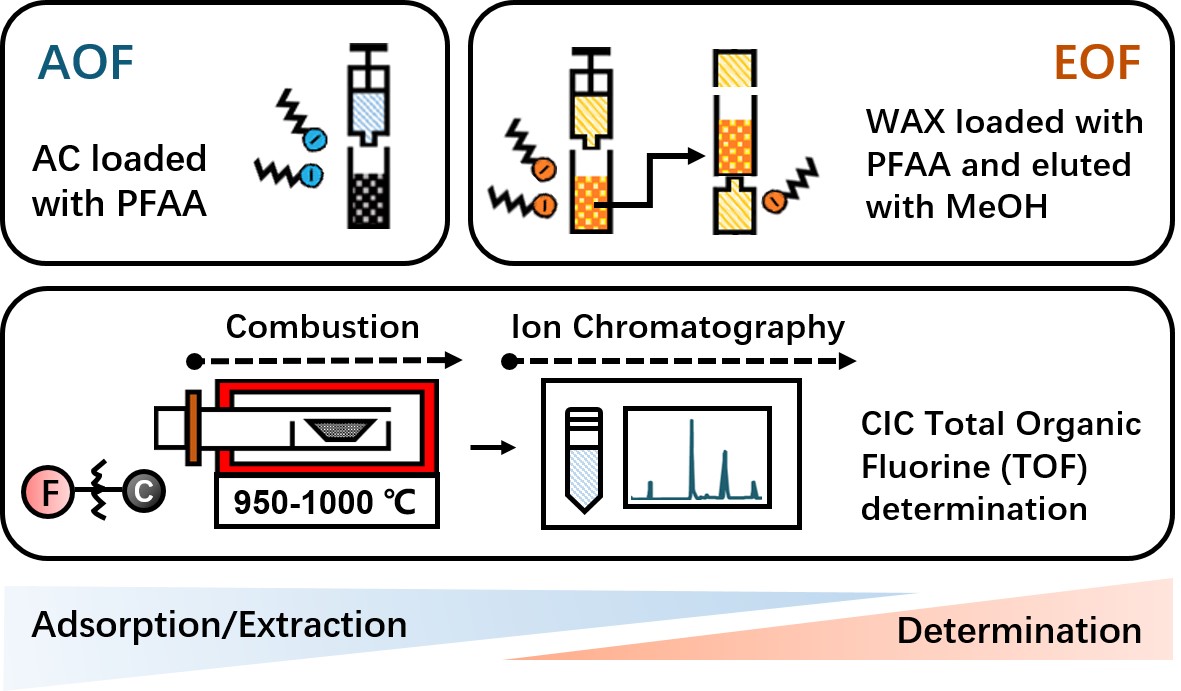
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) are environmental contaminants of concern. Techniques that quantify total organic fluorine (TOF) such as the adsorbable organic fluorine (AOF) and extractable organic fluorine (EOF) methods are important for PFAS risk assessments. The objective of this study was to systematically evaluate each step of the AOF (loading, washing, combustion) and EOF (loading, washing, elution, combustion) methods for the recovery of ten ultrashort-, short-, and long-chain unsubstituted perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs). We measured the overall recovery of fluoride for each method for each PFAA, and the recovery of each PFAA around the loading, washing, and elution steps. We also measured the combustion efficiency of each PFAA by direct combustion. The overall AOF and EOF recovery ranged from 9.3%-103.3% and 21.0%-108.1%, respectively, with higher recoveries measured for PFAAs with increasing chain length in both methods. The three ultrashort-chain PFAAs (trifluoroacetic acid, perfluoropropionic acid, and perfluoropropanesulfonic acid) exhibited the lowest overall recoveries from 9.3-25.2% for AOF and 21.0-51.5% for EOF. We found that decreases in the overall recovery are the result of losses of ultrashort- and short-chain PFAAs during the washing step and the incomplete mineralization of perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids during combustion for AOF and incomplete elution of short- and long-chain PFAAs and the loss of ultrashort-chain PFAAs during the washing step for EOF. Our data suggest that the EOF method is more appropriate than the AOF method for measuring TOF in samples containing ultrashort- and short-chain PFAAs and that methodological improvements are possible with a focus on the washing, elution, and combustion steps.
Keywords PFAS; TOF; AOF; EOF; combustion ion chromatography (CIC); ultrashort-chain PFASs
Publication Water Research